Introduction to Luxury Yacht Interior Design
Luxury yacht interior design is an art form that combines superior craftsmanship, innovative technology, and sumptuous aesthetics to create floating palaces. The design of a yacht’s interior is not merely about aesthetic appeal; it encompasses functionality, comfort, and customization, reflecting the personality and lifestyle of the owner. The process involves architects, designers, engineers, and artisans, each bringing expertise to ensure the final result is both beautiful and seaworthy.
Understanding Yacht Interior Layouts
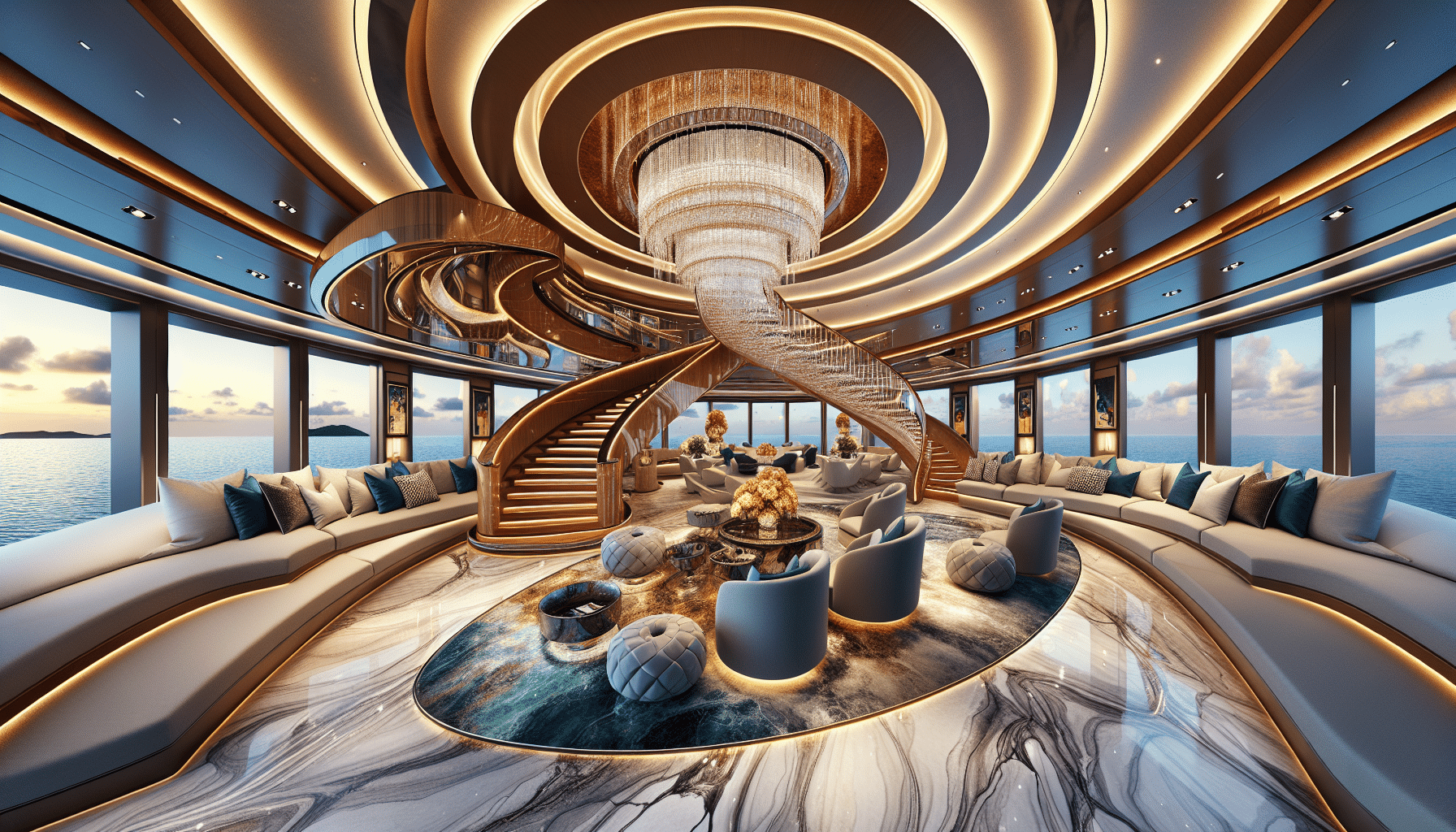
The layout of a luxury yacht is meticulously planned to maximize space and functionality. Common areas include lounges, dining rooms, and ample deck space, while private quarters are designed for comfort and privacy. The challenge lies in balancing open social spaces with more intimate, private areas on a vessel where every inch counts.
Main Deck and Saloon
The main deck typically houses the saloon, a spacious area designed for entertainment and relaxation. Here, designers might incorporate custom-made furniture, state-of-the-art entertainment systems, and elaborate decorative elements. Natural light is a crucial component, often maximized through large panoramic windows or sophisticated lighting systems that mimic natural light.
Accommodations
Sleeping quarters on luxury yachts resemble high-end hotel suites. Each cabin is often equipped with its own bathroom, and the materials used range from fine woods and marbles to exotic leathers and bespoke fabrics. Master suites take luxury to another level with features like king-sized beds, walk-in closets, and spa-like bathrooms.
Materials and Craftsmanship
Yacht interiors deploy materials that reflect opulence while providing durability and comfort. Hardwoods, marble, quartz, and bespoke textiles are commonly used. Craftsmanship is paramount, with impeccable attention to detail in the joinery, upholstery, and fittings. Each element is custom-made to withstand the marine environment while exuding luxury.
Innovative Use of Technology
Modern yachts are equipped with the latest technology, not just for navigation and safety but also for comfort and convenience. Automated systems for lighting, climate control, and entertainment are common. High-end sound systems and acoustics also receive special attention to ensure optimal audio quality is maintained throughout the vessel.
Thematic and Custom Designs
Many yacht owners opt for a bespoke interior theme that reflects their personal taste or a desired ambiance. This can range from minimalist modern designs that focus on space and light to more traditional and ornate settings that evoke a sense of classic luxury. Themes can extend to bespoke art collections, custom sculptures, and unique feature pieces that add a personal touch.
Challenges of Space and Storage
Due to the limited space on yachts, designers must be adept in creating innovative storage solutions. Every element of the interior design is planned to maximize space without compromising on aesthetics or functionality. Hidden compartments, multi-functional furniture, and built-in features are cleverly incorporated to ensure every space is fully utilized.
The Role of Lighting in Yacht Interiors
Lighting design is crucial in yacht interiors, influencing both the ambiance and functionality of spaces. LED lighting is favored for its efficiency and durability, often used to highlight architectural features or artwork, while dimmable solutions are used to create different moods throughout the day and night.
Luxury with Sustainability
As environmental concerns continue to grow, luxury yacht designs increasingly incorporate sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and technologies that minimize the environmental impact of yachting.